Well Coderz, Today we will be solving Pointers in C HackerRank Solution.

Objective
In this challenge, you will learn to implement the basic functionalities of pointers in C. A pointer in C is a way to share a memory address among different contexts (primarily functions). They are primarily used whenever a function needs to modify the content of a variable that it does not own.
In order to access the memory address of a variable, val, prepend it with & sign. For example, &val returns the memory address of val.
This memory address is assigned to a pointer and can be shared among various functions. For example, int *p = &val will assign the memory address of val to pointer p. To access the content of the memory to which the pointer points, prepend it with a *. For example, *p will return the value reflected by val and any modification to it will be reflected at the source (val).
void increment(int *v) {
(*v)++;
}
int main() {
int a;
scanf("%d", &a);
increment(&a);
printf("%d", a);
return 0;
}
Task
Complete the function void update(int *a,int *b). It receives two integer pointers, int* a and int* b. Set the value of a to their sum, b and to their absolute difference. There is no return value, and no return statement is needed.
- a’ = a+b
- b’ = |a-b|
Input Format
The input will contain two integers, a and b, separated by a newline.
Output Format
Modify the two values in place and the code stub main() will print their values.
Note: Input/output will be automatically handled. You only have to complete the function described in the ‘task’ section.
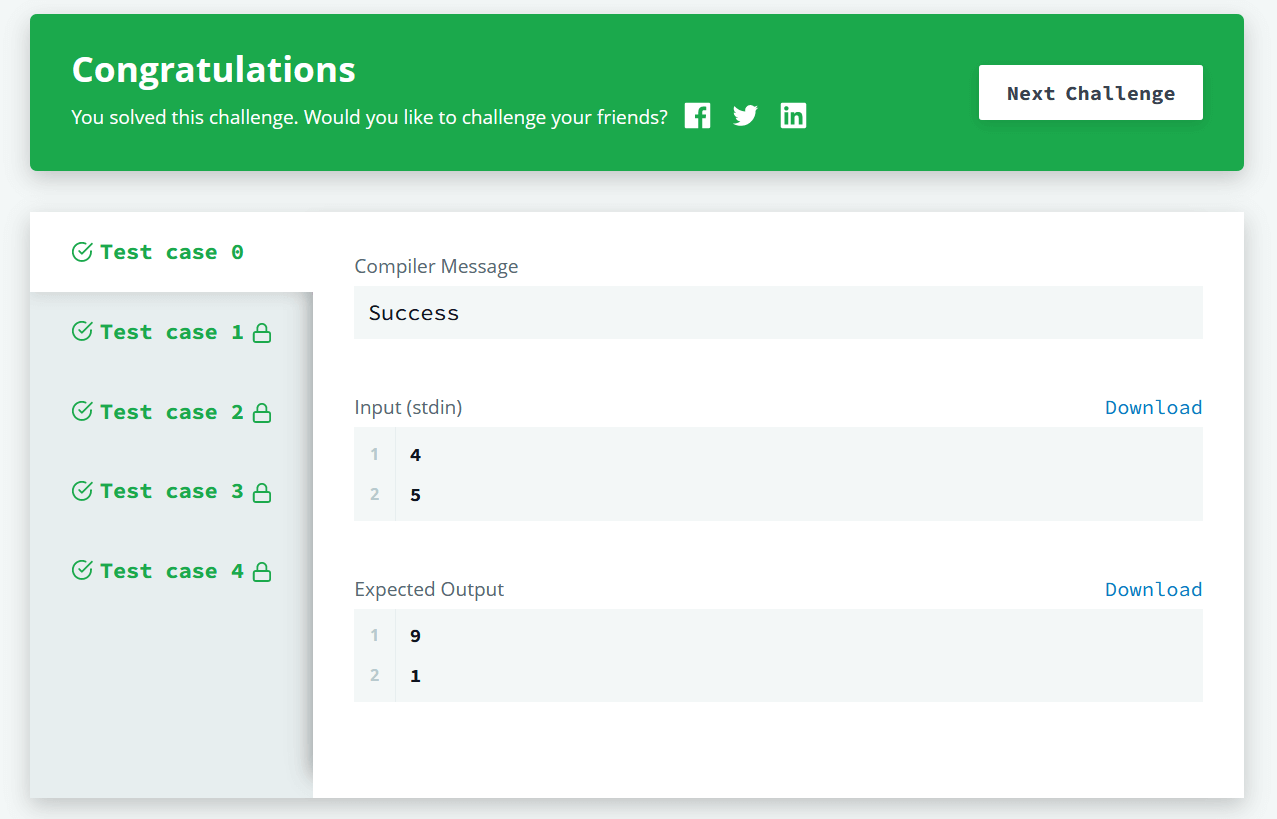
Sample Input
4
5
Sample Output
9
1
Explanation
- a’ = 4 + 5 = 9
- b’ = | 4 – 5 | = 1
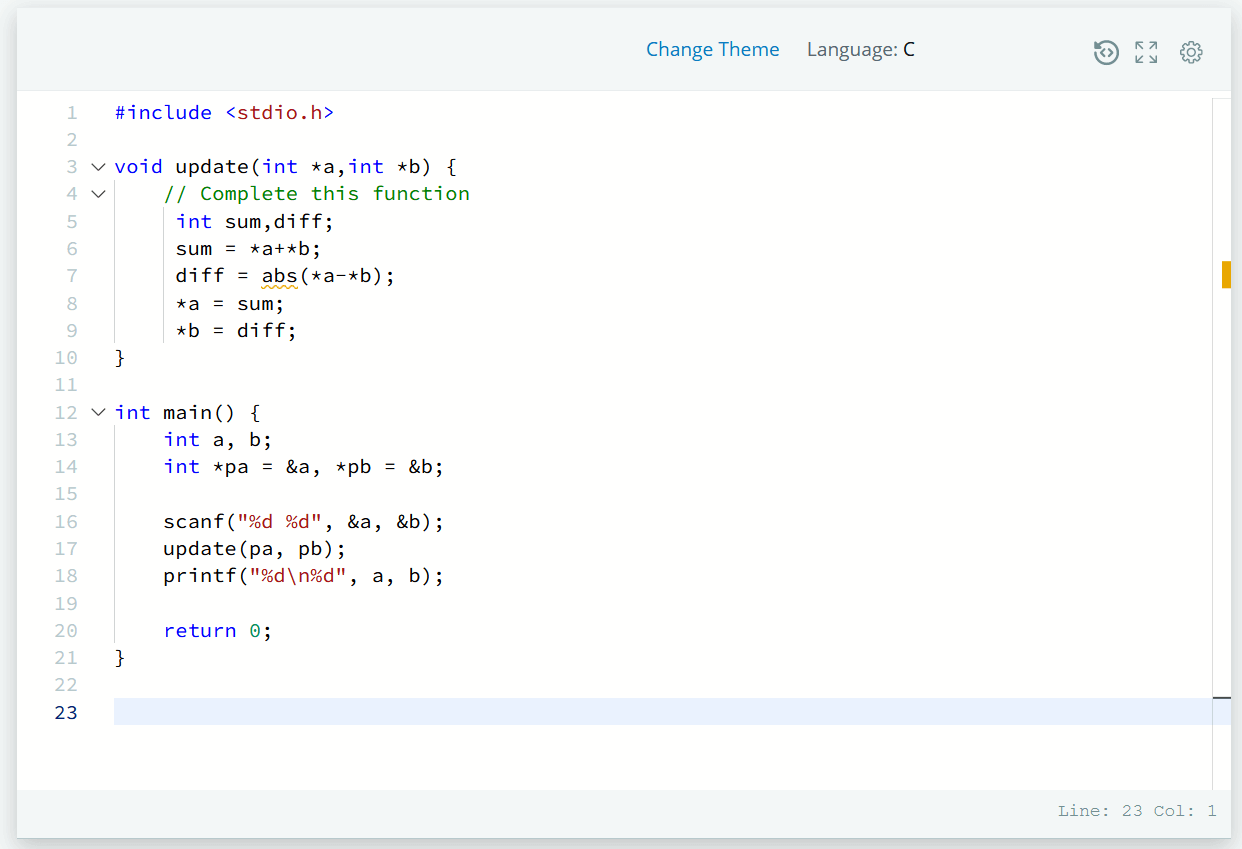
Solution – Pointers in C HackerRank Solution
#include <stdio.h>
void update(int *a,int *b) {
// Complete this function
int sum,diff;
sum = *a+*b;
diff = abs(*a-*b);
*a = sum;
*b = diff;
}
int main() {
int a, b;
int *pa = &a, *pb = &b;
scanf("%d %d", &a, &b);
update(pa, pb);
printf("%d\n%d", a, b);
return 0;
}
Disclaimer: The above Problem (Pointers in C) is generated by Hacker Rank but the Solution is provided by CodingBroz.
Broz Who Code
CodingBroz
#include
void update(int *,int *);
// Complete this function
int main()
{
int a, b;
update(&a, &b);
printf(“%d\n%d”, a, b);
return 0;
}
void update(int *a, int *b)
{
int x,y;
scanf(“%d\n%d”, &x, &y);
*a = x+y;
*b= abs(x-y);
}
What is abs for?
abs(x-y);
abs means it takes a absolute of both x,y=> |x-y|