Hello Coders! Welcome to codingbroz and our Data Structures and algorithm interview series.
Today, we are going to see an interesting problem commonly asked in coding interviews is How to implement a stack using linked list ? We will also implement the code in Java as well as C++ programming language.
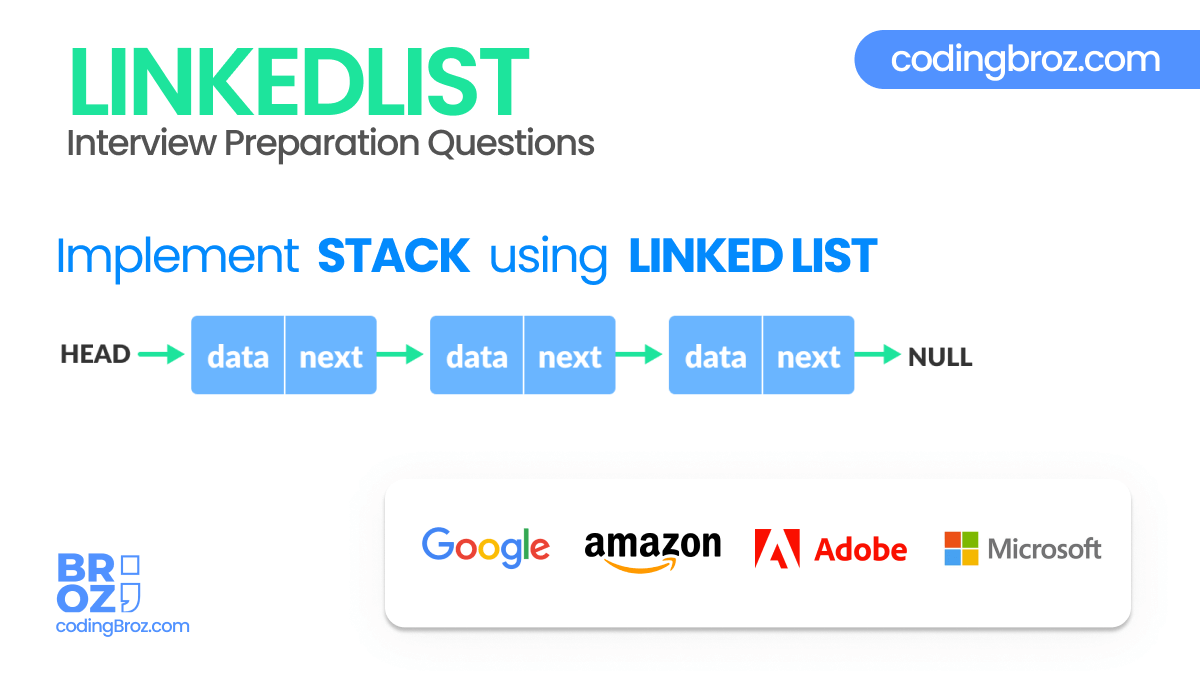
Problem :
The problem statement says that, you have to implement a stack using linked list.
You have to implement the LIFO property of stack using the linked list data structure.
You have to implement the following functions using a linked list which follows the LIFO property of stack :
- push() : This function should accept data in LIFO manner.
- pop() : This function should return and remove data in LIFO manner.
- peek() : This function should return the data in LIFO manner.
Also Read : How to implement a queue using linked list – Java & C++
Solution – How to implement a stack using linked list
Java
// Java program to Implement a stack
// using singly linked list
// import package
import static java.lang.System.exit;
// Create Stack Using Linked list
class StackUsingLinkedlist {
// A linked list node
private class Node {
int data; // integer data
Node link; // reference variable Node type
}
// create global top reference variable global
Node top;
// Constructor
StackUsingLinkedlist()
{
this.top = null;
}
// Utility function to add an element x in the stack
public void push(int x) // insert at the beginning
{
// create new node temp and allocate memory
Node temp = new Node();
// check if stack (heap) is full. Then inserting an
// element would lead to stack overflow
if (temp == null) {
System.out.print("\nHeap Overflow");
return;
}
// initialize data into temp data field
temp.data = x;
// put top reference into temp link
temp.link = top;
// update top reference
top = temp;
}
// Utility function to check if the stack is empty or not
public boolean isEmpty()
{
return top == null;
}
// Utility function to return top element in a stack
public int peek()
{
// check for empty stack
if (!isEmpty()) {
return top.data;
}
else {
System.out.println("Stack is empty");
return -1;
}
}
// Utility function to pop top element from the stack
public void pop() // remove at the beginning
{
// check for stack underflow
if (top == null) {
System.out.print("\nStack Underflow");
return;
}
// update the top pointer to point to the next node
top = (top).link;
}
public void display()
{
// check for stack underflow
if (top == null) {
System.out.printf("\nStack Underflow");
exit(1);
}
else {
Node temp = top;
while (temp != null) {
// print node data
System.out.printf("%d->", temp.data);
// assign temp link to temp
temp = temp.link;
}
}
}
}
// main class
public class CB {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// create Object of Implementing class
StackUsingLinkedlist obj = new StackUsingLinkedlist();
// insert Stack value
obj.push(11);
obj.push(22);
obj.push(33);
obj.push(44);
// print Stack elements
obj.display();
// print Top element of Stack
System.out.printf("\nTop element is %d\n", obj.peek());
// Delete top element of Stack
obj.pop();
obj.pop();
// print Stack elements
obj.display();
// print Top element of Stack
System.out.printf("\nTop element is %d\n", obj.peek());
}
}
C++
// C++ program to Implement a stack
//using singly linked list
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Declare linked list node
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node* link;
};
struct Node* top;
// Utility function to add an element
// data in the stack insert at the beginning
void push(int data)
{
// Create new node temp and allocate memory
struct Node* temp;
temp = new Node();
// Check if stack (heap) is full.
// Then inserting an element would
// lead to stack overflow
if (!temp)
{
cout << "\nHeap Overflow";
exit(1);
}
// Initialize data into temp data field
temp->data = data;
// Put top pointer reference into temp link
temp->link = top;
// Make temp as top of Stack
top = temp;
}
// Utility function to check if
// the stack is empty or not
int isEmpty()
{
return top == NULL;
}
// Utility function to return top element in a stack
int peek()
{
// Check for empty stack
if (!isEmpty())
return top->data;
else
exit(1);
}
// Utility function to pop top
// element from the stack
void pop()
{
struct Node* temp;
// Check for stack underflow
if (top == NULL)
{
cout << "\nStack Underflow" << endl;
exit(1);
}
else
{
// Top assign into temp
temp = top;
// Assign second node to top
top = top->link;
// Destroy connection between
// first and second
temp->link = NULL;
// Release memory of top node
free(temp);
}
}
// Function to print all the
// elements of the stack
void display()
{
struct Node* temp;
// Check for stack underflow
if (top == NULL)
{
cout << "\nStack Underflow";
exit(1);
}
else
{
temp = top;
while (temp != NULL)
{
// Print node data
cout << temp->data << "-> ";
// Assign temp link to temp
temp = temp->link;
}
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Push the elements of stack
push(11);
push(22);
push(33);
push(44);
// Display stack elements
display();
// Print top element of stack
cout << "\nTop element is "
<< peek() << endl;
// Delete top elements of stack
pop();
pop();
// Display stack elements
display();
// Print top element of stack
cout << "\nTop element is "
<< peek() << endl;
return 0;
}
More Problems related to Linked List –
- How to find middle in a LinkedList ?
- How to implement queue data structure using linked list ?
- How to find the k-th element from the end in a given linked list ?