Well coders,
Today we will be solving Box It in C++ HackerRank Solution.

Objective
Design a class named Box whose dimensions are integers and private to the class. The dimensions are labelled: length l, breadth b, and height h.
The default constructor of the class should initialize l, b, and h to 0.
The parameterized constructor Box(int length l, int breadth b, int height h) should initialize Box’s and to length, breadth and height.
The copy constructor Box (Box B) should set l , b and h to B’s l , b and h, respectively.
Apart from the above, the class should have 4 functions:
- int getLength() – Return box’s length
- int getBreadth() – Return box’s breadth
- int getHeight() – Return box’s height
- long long CalculateVolume() – Return the volume of the box
Overload the operator < for the class Box. Box A < Box B if:
- A.l < B.l
- A.b < B.b and A.l == B.l
- A.h < B.h and A.b == B.b and A.l == B.l
Overload operator << for the class Box().
If B is an object of class Box:
cout << B should print B.l, B.b and B.h on a single line separated by spaces.\
For example,
Box b1; // Should set b1.l = b1.b = b1.h = 0;
Box b2(2, 3, 4); // Should set b1.l = 2, b1.b = 3, b1.h = 4;
b2.getLength(); // Should return 2
b2.getBreadth(); // Should return 3
b2.getheight(); // Should return 4
b2.CalculateVolume(); // Should return 24
bool x = (b1 < b2); // Should return true based on the conditions given
cout<<b2; // Should print 2 3 4 in order.
Constraints
0 <= l,b,h <= 105
Two boxes being compared using the < operator will not have all three dimensions equal.
Solution – Box It In C++ HackerRank Solution
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//Implement the class Box
//l,b,h are integers representing the dimensions of the box
// The class should have the following functions :
// Constructors:
// Box();
// Box(int,int,int);
// Box(Box);
// int getLength(); // Return box's length
// int getBreadth (); // Return box's breadth
// int getHeight (); //Return box's height
// long long CalculateVolume(); // Return the volume of the box
//Overload operator < as specified
//bool operator<(Box& b)
//Overload operator << as specified
//ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, Box& B)
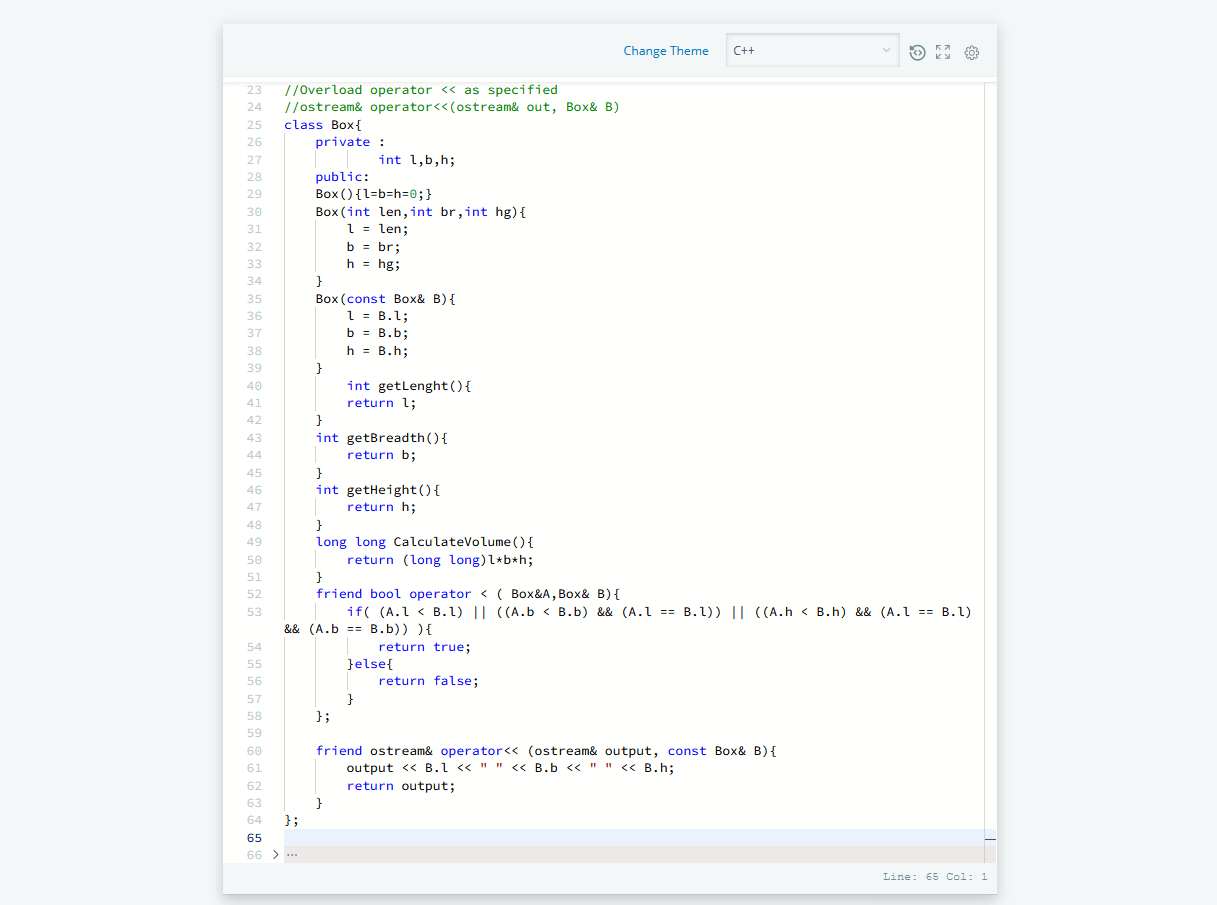
class Box{
private :
int l,b,h;
public:
Box(){l=b=h=0;}
Box(int len,int br,int hg){
l = len;
b = br;
h = hg;
}
Box(const Box& B){
l = B.l;
b = B.b;
h = B.h;
}
int getLenght(){
return l;
}
int getBreadth(){
return b;
}
int getHeight(){
return h;
}
long long CalculateVolume(){
return (long long)l*b*h;
}
friend bool operator < ( Box&A,Box& B){
if( (A.l < B.l) || ((A.b < B.b) && (A.l == B.l)) || ((A.h < B.h) && (A.l == B.l) && (A.b == B.b)) ){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
};
friend ostream& operator<< (ostream& output, const Box& B){
output << B.l << " " << B.b << " " << B.h;
return output;
}
};
void check2()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
Box temp;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
int type;
cin>>type;
if(type ==1)
{
cout<<temp<<endl;
}
if(type == 2)
{
int l,b,h;
cin>>l>>b>>h;
Box NewBox(l,b,h);
temp=NewBox;
cout<<temp<<endl;
}
if(type==3)
{
int l,b,h;
cin>>l>>b>>h;
Box NewBox(l,b,h);
if(NewBox<temp)
{
cout<<"Lesser\n";
}
else
{
cout<<"Greater\n";
}
}
if(type==4)
{
cout<<temp.CalculateVolume()<<endl;
}
if(type==5)
{
Box NewBox(temp);
cout<<NewBox<<endl;
}
}
}
int main()
{
check2();
}
Disclaimer: The above Problem (Box It!) is generated by Hacker Rank but the Solution is provided by CodingBroz.
Broz Who Code
CodingBroz