Today we will be solving Basic Data Types in C++ Hackerrank Problem. After going through this post you will get to know about different types of data types and how to implement them in your respective programs.
Introduction
Some C++ data types, their format specifiers, and their most common bit widths are as follows:
Int (“%d”): 32 Bit integer
Long (“%ld”): 64 bit integer
Char (“%c”): Character type
Float (“%f”): 32 bit real value
Double (“%lf”): 64 bit real value
Reading
To read a data type, use the following syntax:
scanf(“`format_specifier`”, &val)
For example, to read a character followed by a double:
char ch;
double d;
scanf(“%c %lf”, &ch, &d);
For the moment, we can ignore the spacing between format specifiers.
Printing
To print a data type, use the following syntax:
printf(“`format_specifier`”, val)
For example, to print a character followed by a double:
char ch = ‘d’;
double d = 234.432;
printf(“%c %lf”, ch, d);
Note: You can also use cin and cout instead of scanf and printf; however, if you are taking a million numbers as input and printing a million lines, it is faster to use scanf and printf.
Input Format
Input consists of the following space-separated values: int, long, char, float, and double, respectively.
Output Format
Print each element on a new line in the same order it was received as input. Note that the floating point value should be correct up to 3 decimal places and the double to 9 decimal places.
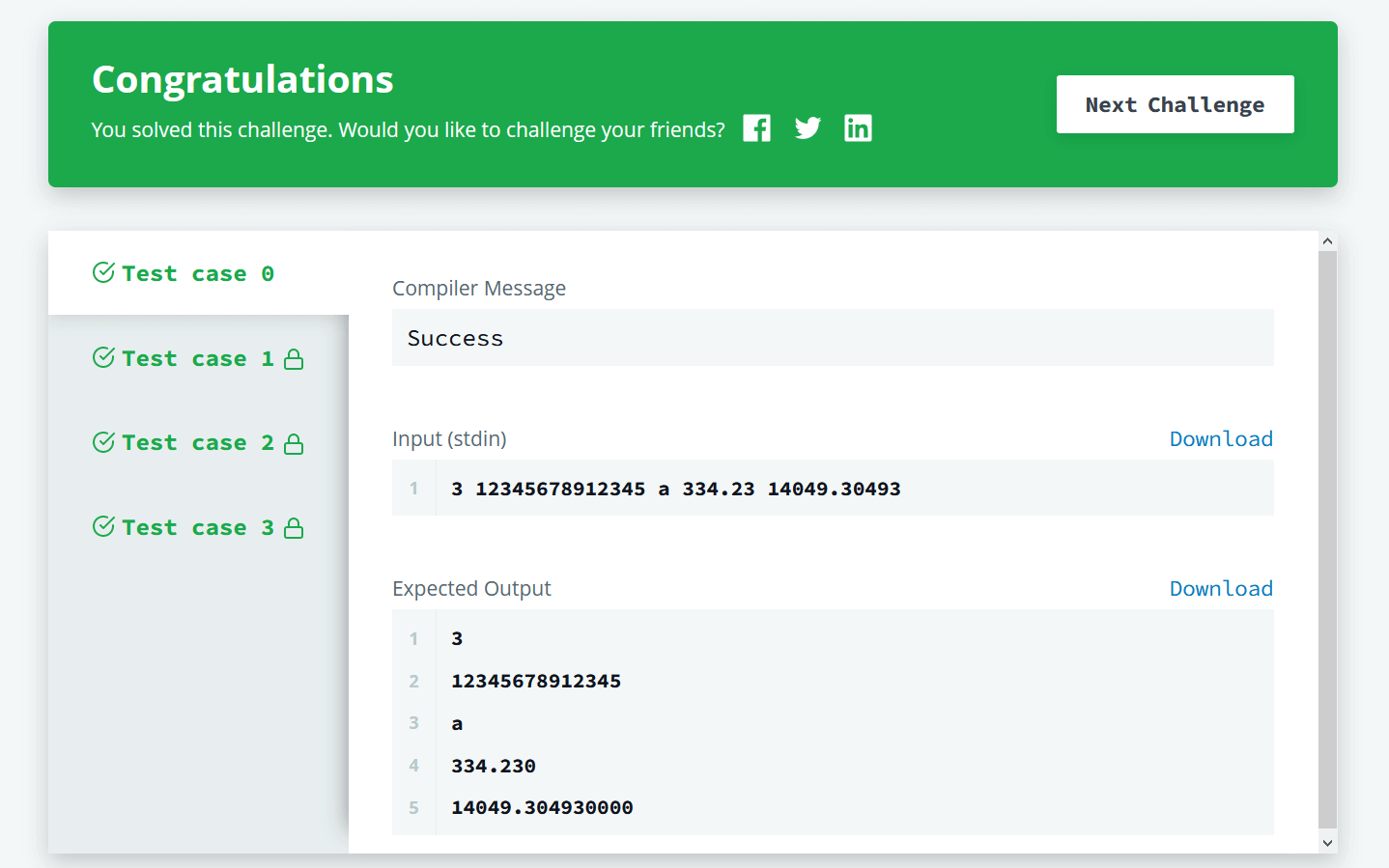
Sample Input
3 12345678912345 a 334.23 14049.30493
Sample Output
3
12345678912345
a
334.230
14049.304930000
Explanation
Print int 3,
followed by long 12345678912345,
followed by char a,
followed by float 334.23,
followed by double 14049.30493.
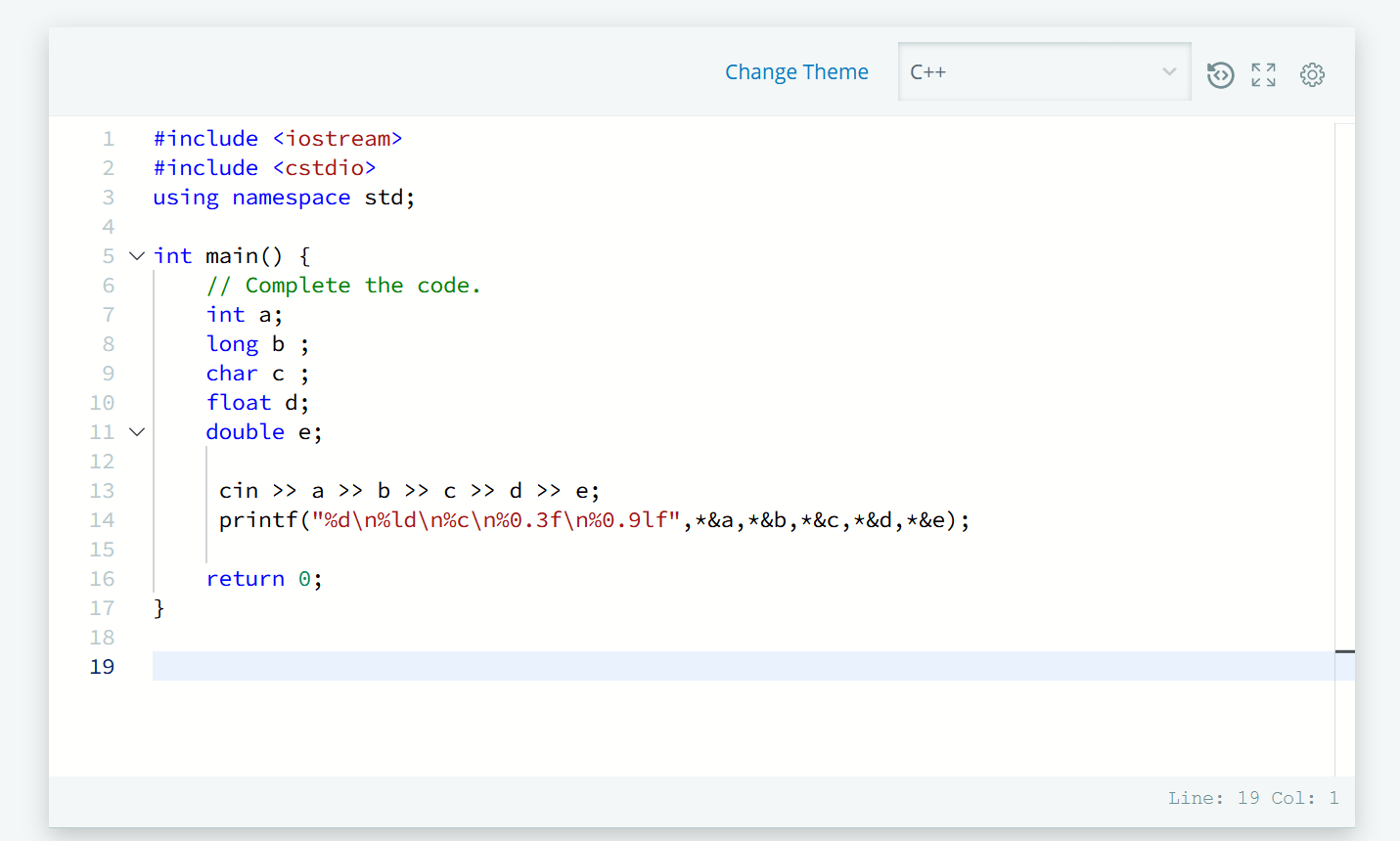
SOLUTION: Basic Data Types in C++
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// Complete the code.
int a;
long b ;
char c ;
float d;
double e;
cin >> a >> b >> c >> d >> e;
printf("%d\n%ld\n%c\n%0.3f\n%0.9lf",*&a,*&b,*&c,*&d,*&e);
return 0;
}
LOGIC EXPLANATION
In this problem you are asked to input 6 variables each of a different data type. As seen in the problem Input and Output it’s easier to take input using cin and cout or you could still use printf and scanf. Now the tricky part is while trying to print the floating and double values. You need to use setprecision() which is available in the iomanip library. To know more about it, click here
If you are using printf to print the float and double variables, you could set the precision in this way
printf(“%.3f”, e); //It prints the floating point accurately up to 3 decimal places.
Above solution is done using printf() function , but we can also use std::setprecision() function
Here is the second code,
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a;
long b;
char c;
float d;
double e;
cin >> a >> b >> c >> d >> e;
cout<< a << '\n' << b << '\n' << c << '\n';
cout << std::fixed << std::setprecision(3) << d << '\n';
cout << std::fixed << std::setprecision(9) << e << '\n';
return 0;
}
Disclaimer: The above problem (Basic Data Types in C++) is generated by Hackerrank but the solution is generated by CodingBroz.
Broz Who Code!!
Notify me what you published about computer programming
why there is use of std::fixed?